Identify the PHI that your organization creates, receives, stores and transmits including PHI shared with consultants, vendors and Business Associates.
HIPAA compliance is a fundamental aspect of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), a federal law mainly focused on protecting sensitive patient health information from being disclosed without the patient's consent or knowledge. The law provides baseline privacy and security standards for the medical information of US citizens.
The standard is applicable to covered entities and their business associates like health care clearinghouses, employer sponsored health plans, health insurers, and medical service providers that engage in certain transactions that involve digital transmission of patient health information (PHI)
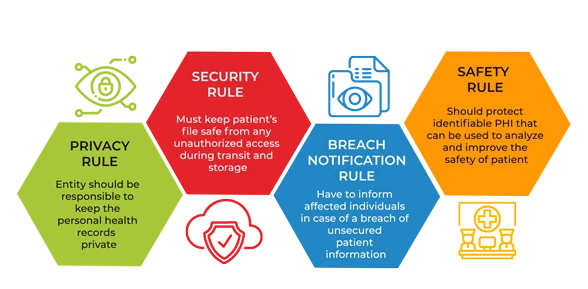
HIPAA Regulation divided into Security Rule, Privacy Rule, Transactions and Code Sets (TCS) Rule, Unique Identifiers Rule, Breach Notification Rule, Omnibus Final Rule. HIPAA Security Rule requires implementation of 1) Administrative, 2) Physical, and 3) Technical safeguards.In Addition, it imposes other organizational requirements and a need to document processes analogous to the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
Office of Civil Rights (OCR), explains the failure to provide a “specific risk analysis methodology” is due to Covered Entities and Business Associates being of different sizes, capabilities and complexity. As per OCR, the key objectives of a HIPAA risk assessment are :
-
-
Identify the human, natural and environmental threats to the integrity of PHI human threats including those which are both intentional and unintentional.
-
Assess what measures are in place to protect against threats to the integrity of PHI, and the likelihood of a “reasonably anticipated” breach occurring.
-
Determine the potential impact of a PHI breach and assign each potential occurrence a risk level based on the average of the assigned likelihood and impact levels.
-
Document the findings and implement measures, procedures and policies where necessary to tick the boxes on the HIPAA compliance checklist and ensure HIPAA compliance.
-
HIPAA risk assessment, the rationale for the measures, procedures and policies subsequently implemented, and all policy documents must be kept for a minimum of six years.
HIPAA Compliance & Certification Approach
QRC follows a well-documented approach to work alongside our clients aiding them in attaining their compliance goals. This require a Well-documented execution plan along with defined milestones.

 +91 9594449393
+91 9594449393 +1 4847906355
+1 4847906355 +63 9208320598
+63 9208320598 +44 1519470017
+44 1519470017 +84 908370948
+84 908370948 +7 9639173485
+7 9639173485 +62 81808037776
+62 81808037776 +90 5441016383
+90 5441016383 +66 993367171
+66 993367171 +254 725235855
+254 725235855 +256 707194495
+256 707194495 +46 700548490
+46 700548490


