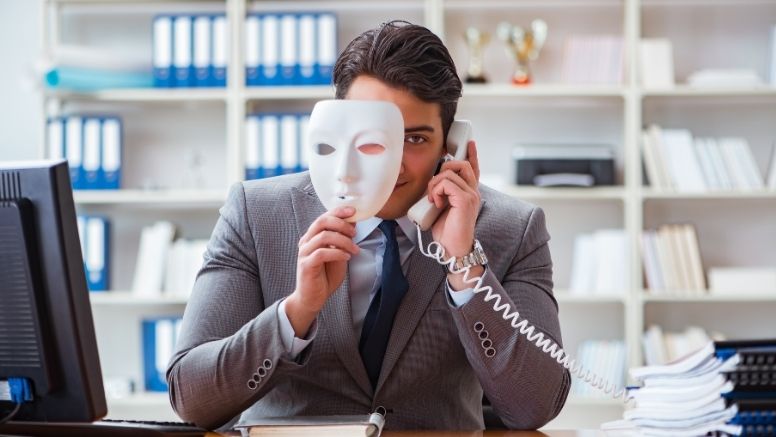
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, safeguarding sensitive financial
information is of utmost importance. This is especially true for businesses,
including call centres and other organizations involved in telephone
transactions, which handle an array of credit and debit card details daily.
Protecting this data from potential threats and fraud is a critical
responsibility that cannot be overlooked. This blog serves as a comprehensive
guide, shedding light on essential strategies and best practices to secure
payment card data effectively in telephone transactions.
Understanding the Stakes
The stakes are high when it comes to securing payment card data during telephone transactions. Call centres and similar setups often deal with sensitive information, including credit card numbers, security codes, and personal identification numbers (PINs). Any compromise of this information can lead to severe financial and reputational consequences for both the organization and its customers.
Adherence to PCI Data Security Standard (DSS)
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a vital framework that provides specific guidelines and requirements for handling cardholder information securely. Compliance with PCI DSS is mandatory for any organization dealing with credit card transactions, including call centres. It encompasses various security measures and practices that must be implemented to ensure the safe handling, storage, and transmission of cardholder data.
Key Considerations and Best Practices
To achieve PCI DSS compliance and effectively secure payment card data in telephone transactions, organizations must implement a combination of measures and best practices. Here are some key considerations:
- Encryption of Data: Implement robust encryption protocols for cardholder data. This ensures that even if the data is intercepted, it remains unreadable and unusable for malicious purposes.
- Access Control and Authentication: Utilize strong access control mechanisms and multi-factor authentication for anyone accessing sensitive payment card information. Limit access only to authorized personnel.
- Regular Monitoring and Auditing: Establish a robust monitoring system to track and log all access and activities related to cardholder data. Regular audits help identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educate employees on data security best practices, social engineering, and potential threats. Well-informed employees are often the first line of defense against cyber-attacks.
- Regular Security Updates and Patch Management: Stay up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates for all systems and software handling payment card data. Vulnerabilities can be exploited if systems are not adequately patched.
- Secure Call Recording Procedures: If call recordings are necessary, employ secure call recording technologies that comply with PCI DSS. Ensure sensitive information is redacted or masked during recordings.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a well-defined incident response plan in place to respond to any security incidents or breaches involving payment card data swiftly and effectively.
The Role of Technology in Compliance
Various technologies and solutions can assist organizations in achieving
PCI DSS compliance and securing payment card data effectively. Automated 'pause
and resume' systems, 'keypad payment by phone' technology, and role-based
log-ins are some of the technological approaches that can help maintain
compliance seamlessly.
BPOs, particularly call centres handling credit and debit card information, bear the responsibility of protecting customers from fraud. Here are four main technology options to achieve PCI compliance :
- Automated 'Pause and Resume' Technology: Requires agents to pause call recordings during payment processing and resume afterward. Relies on agent intervention, making it cost-effective but potentially prone to human error.
- 'Keypad Payment by Phone' Technology: Allows customers to enter their card details using their phone keypad, masking sensitive information from both agents and recordings, enhancing PCI compliance.
- Automated 'Mute and Unmute' Technology: Mutes audio during payment processing, ensuring sensitive data isn't recorded. However, subsequent recordings may only contain silence or audible tones.
- Integration with Call Recording System via API: Alters agent applications, triggering call recording pause and resume through scripted instructions, minimizing the risk of human error.
Securing payment card data in telephone transactions is not just a legal
requirement it's a responsibility to protect the privacy and financial
well-being of both organizations and customers. Adherence to PCI DSS and the
implementation of robust security measures are crucial steps in achieving this
security. By investing in the right technologies and educating employees,
businesses can create a safer payment ecosystem, reinforcing trust and
confidence among their customer bases.
Remember, in the realm of financial transactions, security is
non-negotiable.

 +91 9594449393
+91 9594449393 +1 4847906355
+1 4847906355 +63 9208320598
+63 9208320598 +44 1519470017
+44 1519470017 +84 908370948
+84 908370948 +7 9639173485
+7 9639173485 +62 81808037776
+62 81808037776 +90 5441016383
+90 5441016383 +66 993367171
+66 993367171 +254 725235855
+254 725235855 +256 707194495
+256 707194495 +46 700548490
+46 700548490.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
